Type 1 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy in India: A Comprehensive Guide
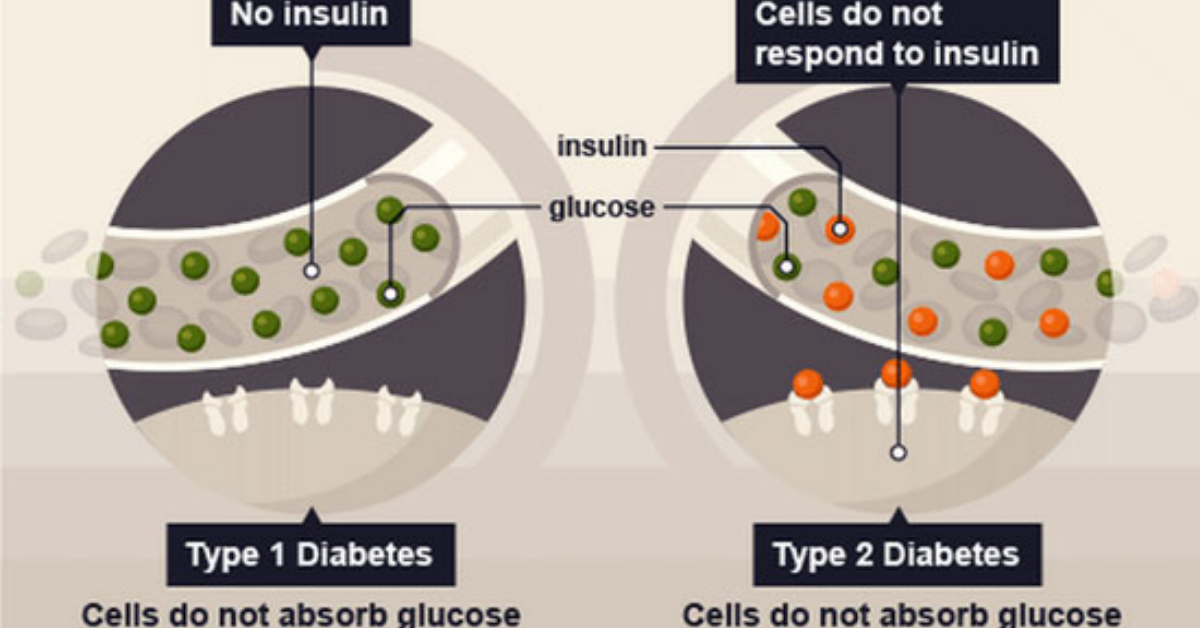
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, a hormone necessary for the proper regulation of blood sugar levels. Unlike Type 2 diabetes, which is often related to lifestyle factors, Type 1 Diabetes Stem Cell Therapy India is an autoimmune disease that typically develops during childhood or adolescence. Managing T1D typically involves daily insulin injections, constant monitoring of blood glucose levels, and a carefully controlled diet.
However, recent advancements in medical science, particularly in stem cell research, have opened up new possibilities for treating Type 1 Diabetes. Stem cell therapy is emerging as a potential treatment to restore insulin production in people with T1D, offering hope for a more permanent solution to the condition. In this article, we will explore how stem cell therapy is being used to treat Type 1 Diabetes in India, the process involved, and what patients can expect.
What is Stem Cell Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes?
Stem cell therapy is a cutting-edge medical treatment that involves the use of stem cells to repair or regenerate damaged tissues and organs. In the context of Type 1 Diabetes, stem cells are used to potentially regenerate insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, which are destroyed in individuals with the disease.
The primary aim of stem cell therapy for Type 1 Diabetes is to restore the body’s ability to produce insulin naturally, which can lead to better blood sugar control and potentially reduce or eliminate the need for insulin injections.
How Does Stem Cell Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes Work?
Stem cell therapy for Type 1 Diabetes typically involves the following steps:
-
Stem Cell Extraction: The first step involves extracting stem cells, which can either come from the patient’s own body (autologous stem cells) or from a donor (allogeneic stem cells). Common sources include bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord blood.
-
Stem Cell Processing: The extracted stem cells are then processed and purified in a laboratory to ensure that only healthy, viable cells are used for the treatment. These stem cells are then prepared for implantation.
-
Stem Cell Transplantation: The purified stem cells are introduced into the patient’s body, typically via an intravenous injection or direct injection into the pancreas or surrounding tissues. The goal is for these stem cells to differentiate into healthy beta cells, which are responsible for insulin production.
-
Regeneration of Beta Cells: Once introduced into the body, the stem cells have the potential to regenerate and restore the function of insulin-producing beta cells. The hope is that these newly formed cells will begin to secrete insulin, regulating blood glucose levels and reducing the need for insulin injections.
-
Monitoring and Follow-up: After the procedure, the patient’s blood sugar levels are closely monitored, and additional treatments may be necessary to encourage the stem cells to properly integrate and begin functioning as beta cells. Ongoing follow-up care is crucial for assessing the success of the therapy.
Why Choose India for Stem Cell Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes?
India is rapidly becoming a hub for medical tourism, with its world-class healthcare facilities offering state-of-the-art treatments at a fraction of the cost compared to Western countries. The country is home to numerous specialized clinics and hospitals that offer stem cell therapy for Type 1 Diabetes.
Here are some reasons why many patients choose India for stem cell therapy:
1. Advanced Medical Infrastructure
India has made significant advancements in the field of regenerative medicine, and many of the country’s hospitals and clinics are equipped with modern technology and equipment. These facilities adhere to international standards and are led by highly qualified and experienced medical professionals.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
The cost of stem cell therapy in India is significantly lower compared to countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, or Canada. This makes it a highly attractive option for international patients seeking affordable treatment options without compromising on quality.
3. Experienced Doctors
India boasts a large pool of skilled and experienced doctors, many of whom have received their training abroad. These professionals specialize in regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapies for various conditions such as Type 1 Diabetes. Their expertise, combined with the advanced technology available, gives patients confidence in the treatment’s safety and efficacy.
4. Personalized Care
Many medical facilities in India provide personalized care tailored to the specific needs of each patient. This includes one-on-one consultations with specialists, comprehensive treatment plans, and post-treatment care, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients.
5. Availability of Support Services
India offers comprehensive support services for international patients, including travel assistance, visa arrangements, and accommodation options near the medical facility. This ensures that patients can focus on their treatment without worrying about logistical issues.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Type 1 Diabetes
Stem cell therapy for Type 1 Diabetes is still in the experimental stages, but early studies and trials have shown promising results. Some potential benefits include:
1. Restored Insulin Production
The primary benefit of stem cell therapy is the potential to restore the pancreas’s ability to produce insulin. This could dramatically improve the quality of life for people with Type 1 Diabetes by reducing their dependence on insulin injections and pumps.
2. Improved Blood Sugar Control
By regenerating insulin-producing beta cells, stem cell therapy may help patients achieve better blood sugar control. This can lead to fewer fluctuations in glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and heart disease.
3. Reduced Risk of Complications
If successful, stem cell therapy could reduce the long-term complications of Type 1 Diabetes by addressing the root cause of the condition—beta cell destruction. By restoring insulin production, stem cell therapy may help prevent or delay complications like diabetic retinopathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular disease.
4. Improved Overall Well-being
With better blood sugar management, patients may experience an improvement in their overall health, energy levels, and quality of life. Stem cell therapy could also reduce the psychological burden of daily insulin injections, offering patients greater freedom and independence.
Risks and Considerations
While stem cell therapy for Type 1 Diabetes offers exciting potential, it is important to note that it is still in the experimental phase, and long-term studies are needed to fully assess its safety and effectiveness. Some risks and considerations include:
-
Immune Rejection: If donor stem cells are used, there is a risk that the body may reject them. This could potentially lead to complications, although immunosuppressive drugs can sometimes be used to reduce this risk.
-
Uncertainty of Results: Not all patients may respond to stem cell therapy in the same way. While some may experience significant improvements in insulin production, others may see little to no effect.
-
Cost and Availability: Although stem cell therapy is more affordable in India, it still involves a significant financial investment. Additionally, the treatment is not universally available and may not be covered by insurance.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy for Type 1 Diabetes is an exciting and innovative treatment option that offers hope for individuals living with this chronic condition. In India, patients have access to world-class medical facilities and highly skilled specialists who are at the forefront of regenerative medicine. While the therapy is still in the early stages of development, the results so far show promise, with many patients experiencing improved blood sugar control and a reduction in their dependency on insulin.